Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes worksheet from EdPlace
What are Bacteria? (with pictures)
Overview of Bacterial Cell Walls A cell wall, not just of bacteria but for all organisms, is found outside of the cell membrane. It's an additional layer that typically provides some strength that the cell membrane lacks, by having a semi-rigid structure.

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
Structure of Bacterial Cell (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the Structure of Bacterial Cell. Bacteria (sing. bacterium) are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms which divide by binary fission.
Bacteria Cell Vector Art, Icons, and Graphics for Free Download
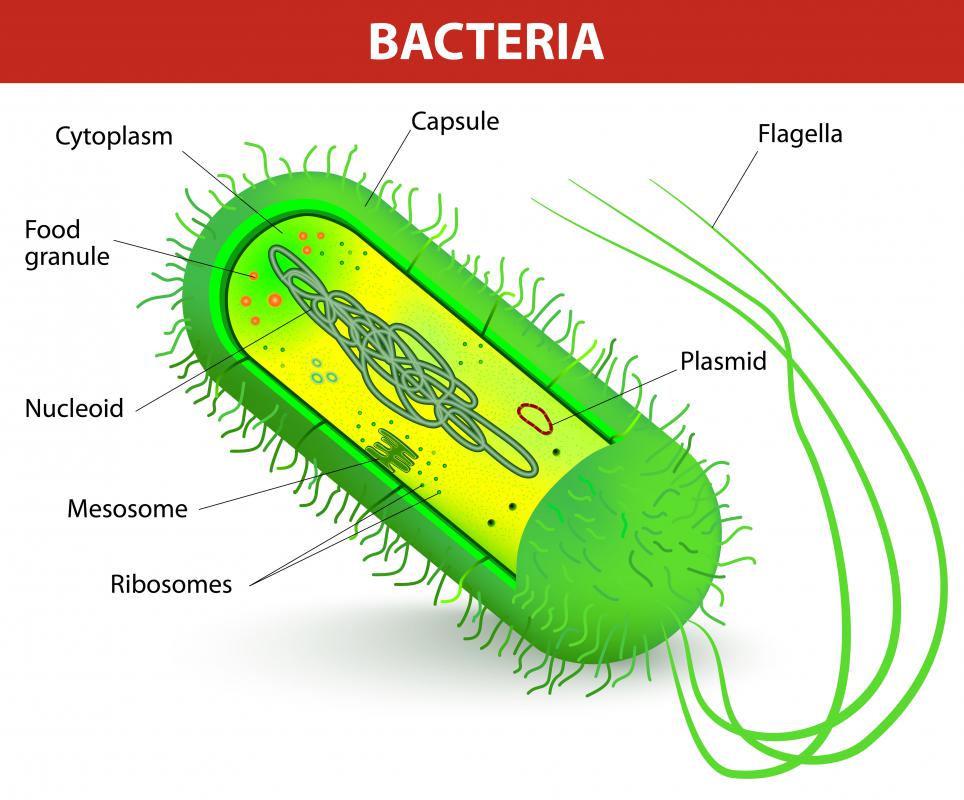
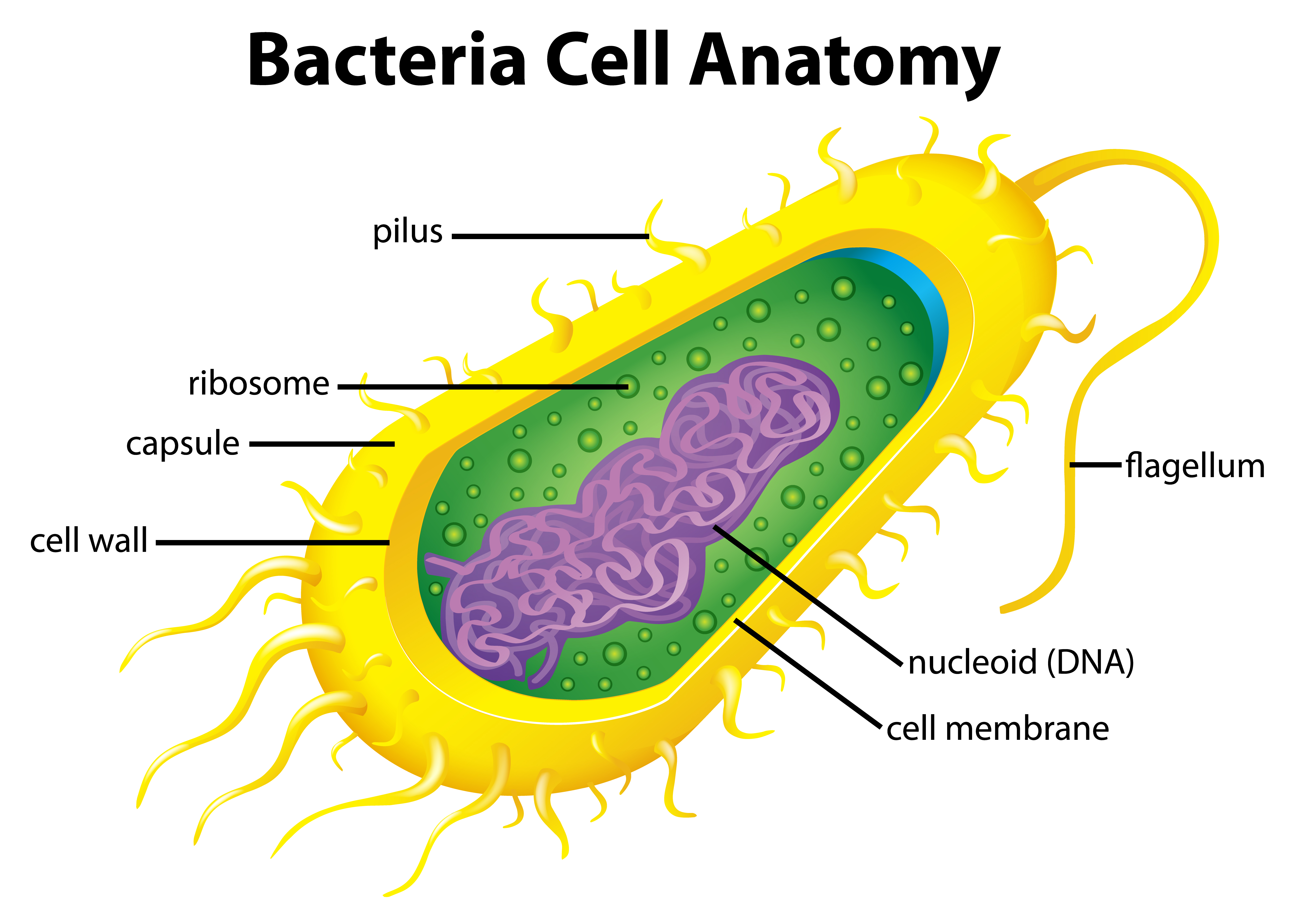
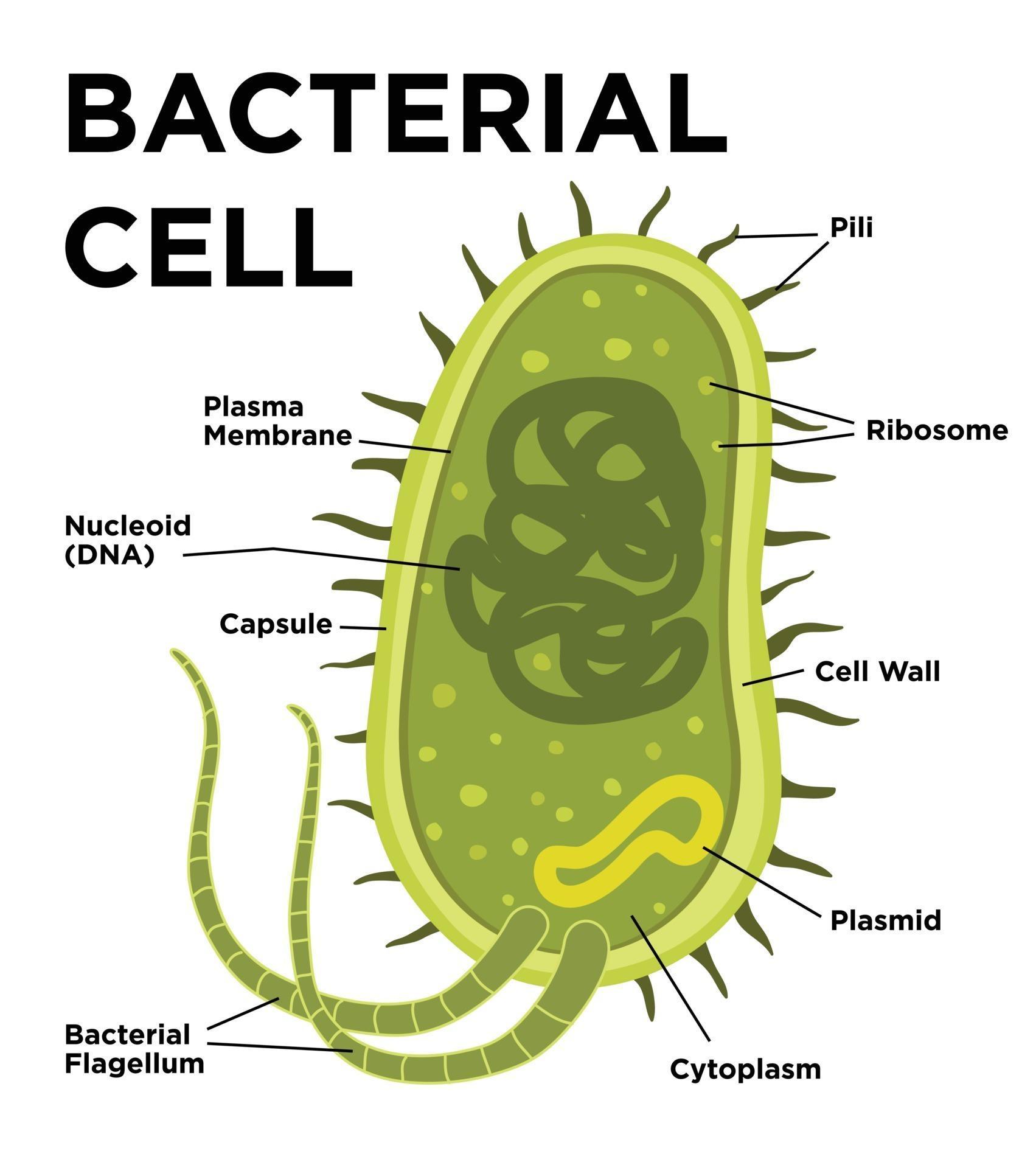
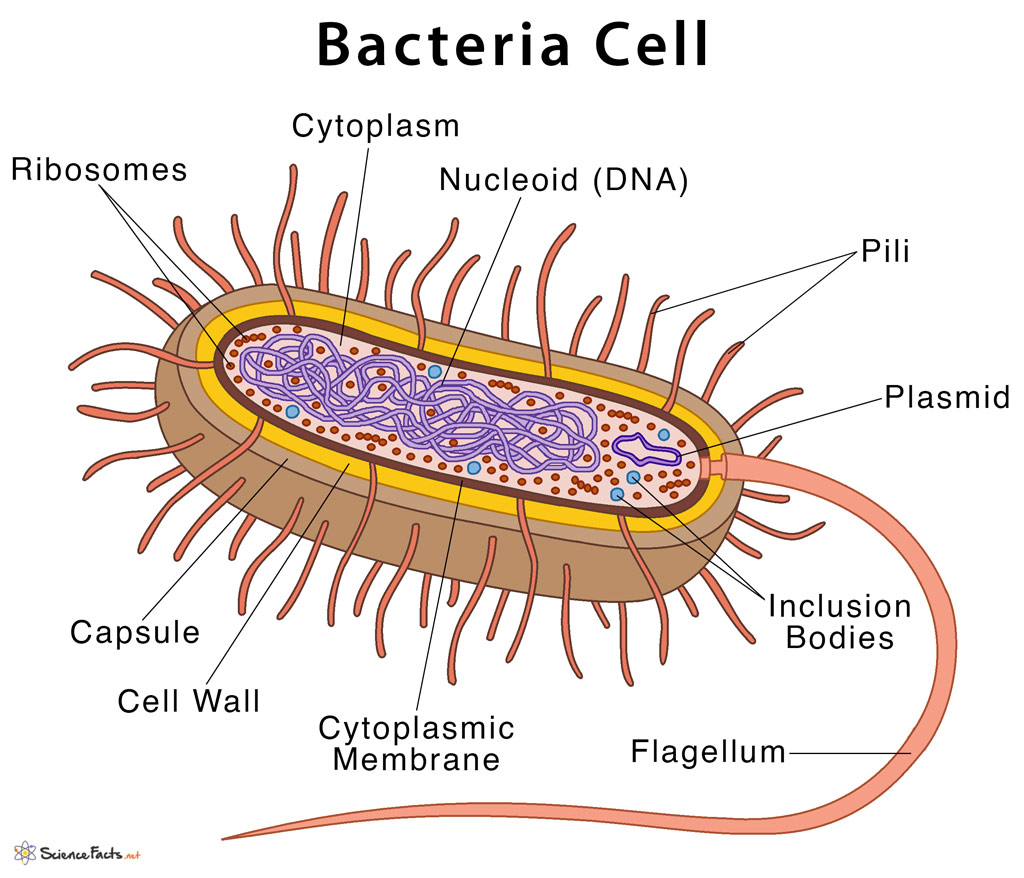
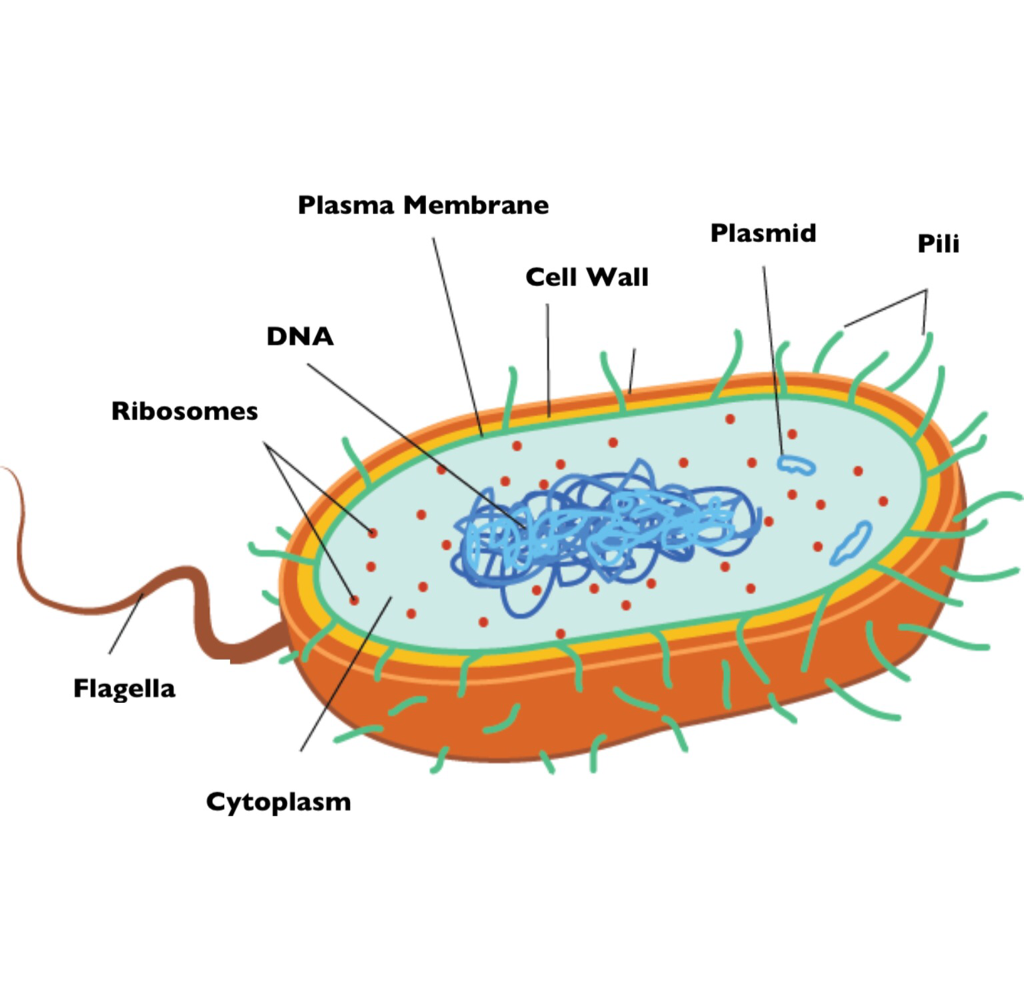
Bacteria is a unicellular prokaryotic organism. The structure of the bacteria consists of three major parts: Outer layer (cell envelope), cell interior, and additional structures. Outer layer (Cell envelope): It includes the cell wall of bacteria and the plasma membrane beneath it.
anatomia da célula bacteriana em estilo simples. ilustração moderna do
Bacteria are classified by shape into three basic groups: cocci, bacilli, and spirochetes (Figure 2-1).The cocci are round, the bacilli are rods, and the spirochetes are spiral-shaped. Some bacteria are variable in shape and are said to be pleomorphic (heterogeneous shape). The shape of a bacterium is determined by its rigid cell wall.

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
Bacteria: Definition & Characteristics With Examples & Diagram Bacteria Cell Bacteria are disease-causing, microscopic, single-celled organisms with prokaryotic cell structures. They do not have membrane-bound organelles, including a true nucleus.
Bacteria Cell Structure
< Prev Next > Chapter 2 Structure Milton R.J. Salton and Kwang-Shin Kim. Go to: General Concepts Gross Morphology Bacteria have characteristic shapes (cocci, rods, spirals, etc.) and often occur in characteristic aggregates (pairs, chains, tetrads, clusters, etc.). These traits are usually typical for a genus and are diagnostically useful.
Bacteria Cell Structure YouTube
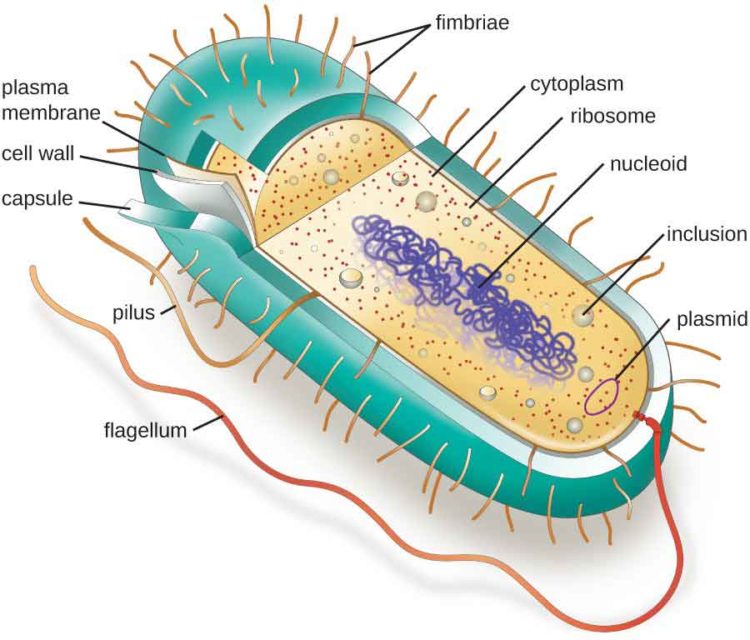
Bacterial cell structure The bacterium, despite its simplicity, contains a well-developed cell structure which is responsible for some of its unique biological structures and pathogenicity. Many structural features are unique to bacteria and are not found among archaea or eukaryotes.

Bacterial Cell Composition
. This means they do not have a nucleus or any other structures which are surrounded by membranes . Larger bacterial cells may be visible using a light microscope, however an electron microscope.

Bacterial Structure Plantlet
Bacterial cell have simpler internal structure. It lacks all membrane bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, lysosome, golgi, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast, peroxisome, glyoxysome, and true vacuole. Bacteria also lacks true membrane bound nucleus and nucleolus. The bacterial nucleus is known as nucleoid.
Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes worksheet from EdPlace
Home Botany Structure and Function of a Typical Bacterial Cell with Diagram Animesh Sahoo August 14, 2021 Bacteria are unicellular. Their structure is a very simple type. Bacteria are prokaryotes because they do not have a well-formed nucleus. A typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to a plant cell.
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
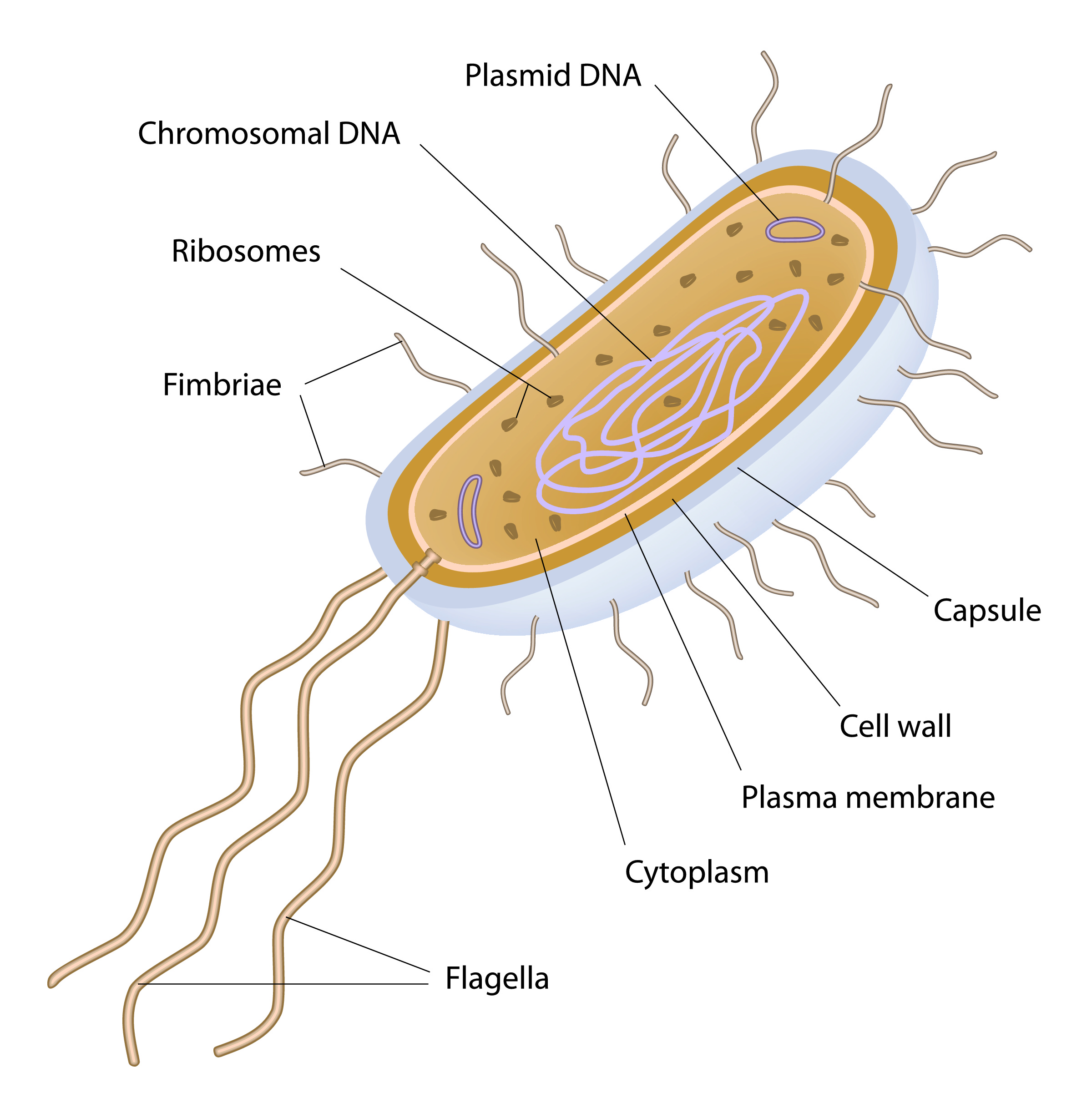
Structure of Bacterial Cell: Bacterial cells (prokaryotic cells) are structurally much simpler than eukaryotic cells and the two cell types are compared in Table 3.2. They consists of various cell surface structures, cell wall, plasma membrane, many cytoplasmic inclusions, and the bacterial chromosome (nucleoid).

Bacteria Diagram
Bacteria are prokaryotic cells that play an important role in human disease and health. They can cause disease but are also part of the human microbiota and.

bacteria Cell, Evolution, & Classification Britannica
bacteria, any of a group of microscopic single-celled organisms that live in enormous numbers in almost every environment on Earth, from deep-sea vents to deep below Earth's surface to the digestive tracts of humans. Bacteria lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other internal structures and are therefore ranked among the unicellular life-forms.
Bacteria Grade 11 Biology Study Guide
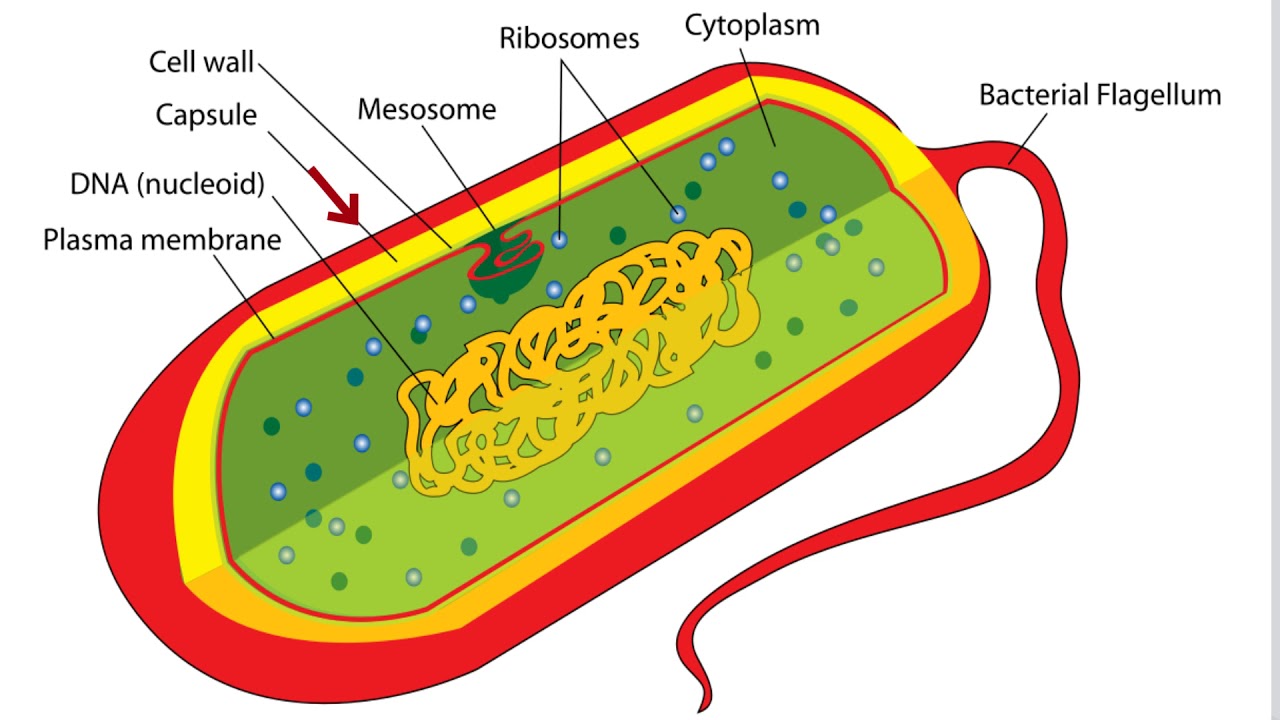
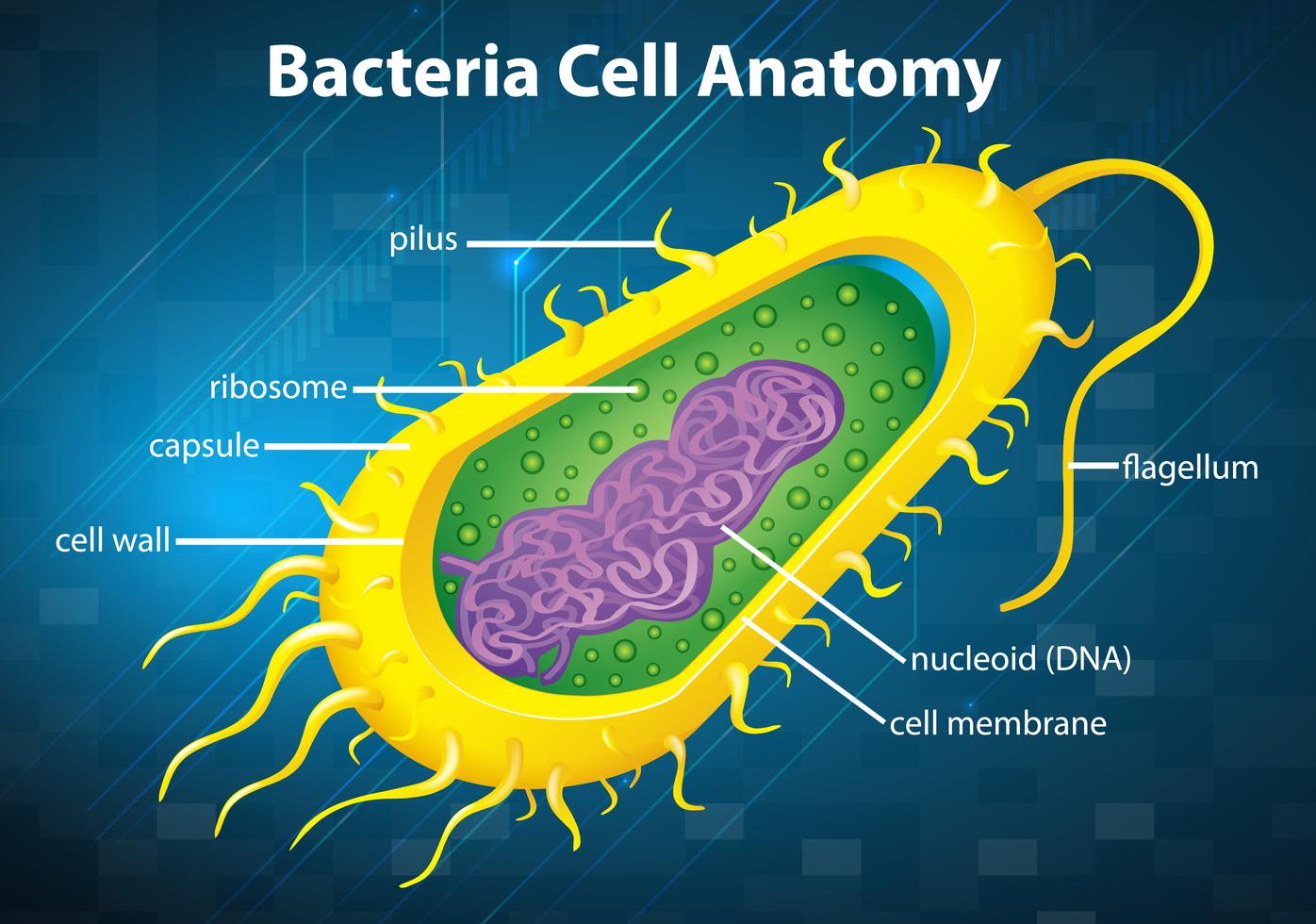
The bacteria diagram given below represents the structure of a typical bacterial cell with its different parts. The cell wall, plasmid, cytoplasm and flagella are clearly marked in the diagram. Bacteria Diagram representing the Structure of Bacteria Ultrastructure of a Bacteria Cell The structure of bacteria is known for its simple body design.
Bacteria cell structure 365530 Vector Art at Vecteezy
volume = 4.2 μm3. r = 2 μm. surface area = 50.3 μm2. volume = 33.5 μm3. The surface-to-volume ratio of the smaller cell is 3, while the surface-to-volume ratio of the larger cell decreases to 1.5. Think of the cell surface as the ability of the cell to bring in nutrients and let out waste products.

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
In this article we will discuss about the cell structure of bacteria with the help of diagrams. A bacterial cell (Fig. 2.5) shows a typical prokaryotic structure. The cytoplasm is enclosed by three layers, the outermost slime or capsule, the middle cell wall and inner cell membrane.