GRAVITY PHENOMENA documentary
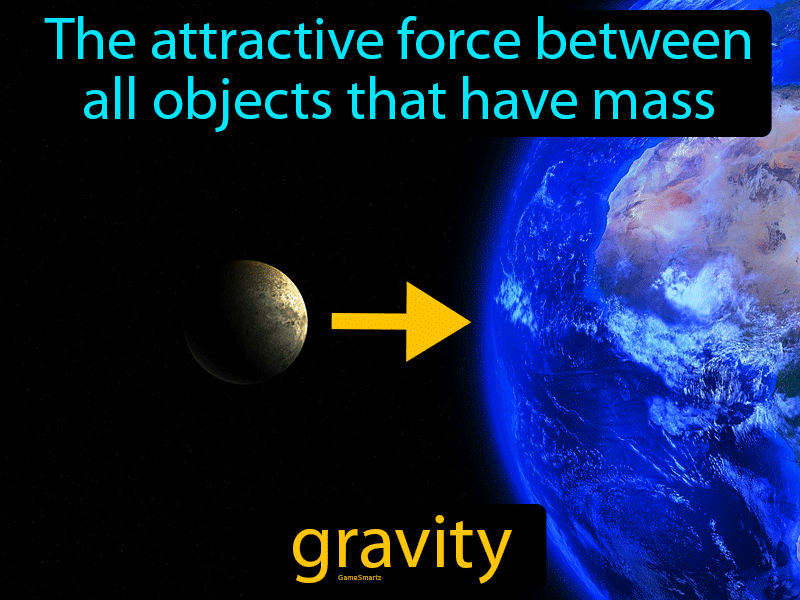
Gravity Definition & Image GameSmartz
In physics, gravity is the natural force that causes things to fall toward the earth. The noun gravity can also mean seriousness or solemnity.

Gravity is mathematically relatable to dynamics of subatomic particles
Gravity is the weakest of the fundamental forces. A bar magnet will electromagnetically pull a paper clip upward, overcoming the gravitational force of the entire Earth on the piece of office.

The Law of Gravity Biology facts, Learn physics, Physics lessons
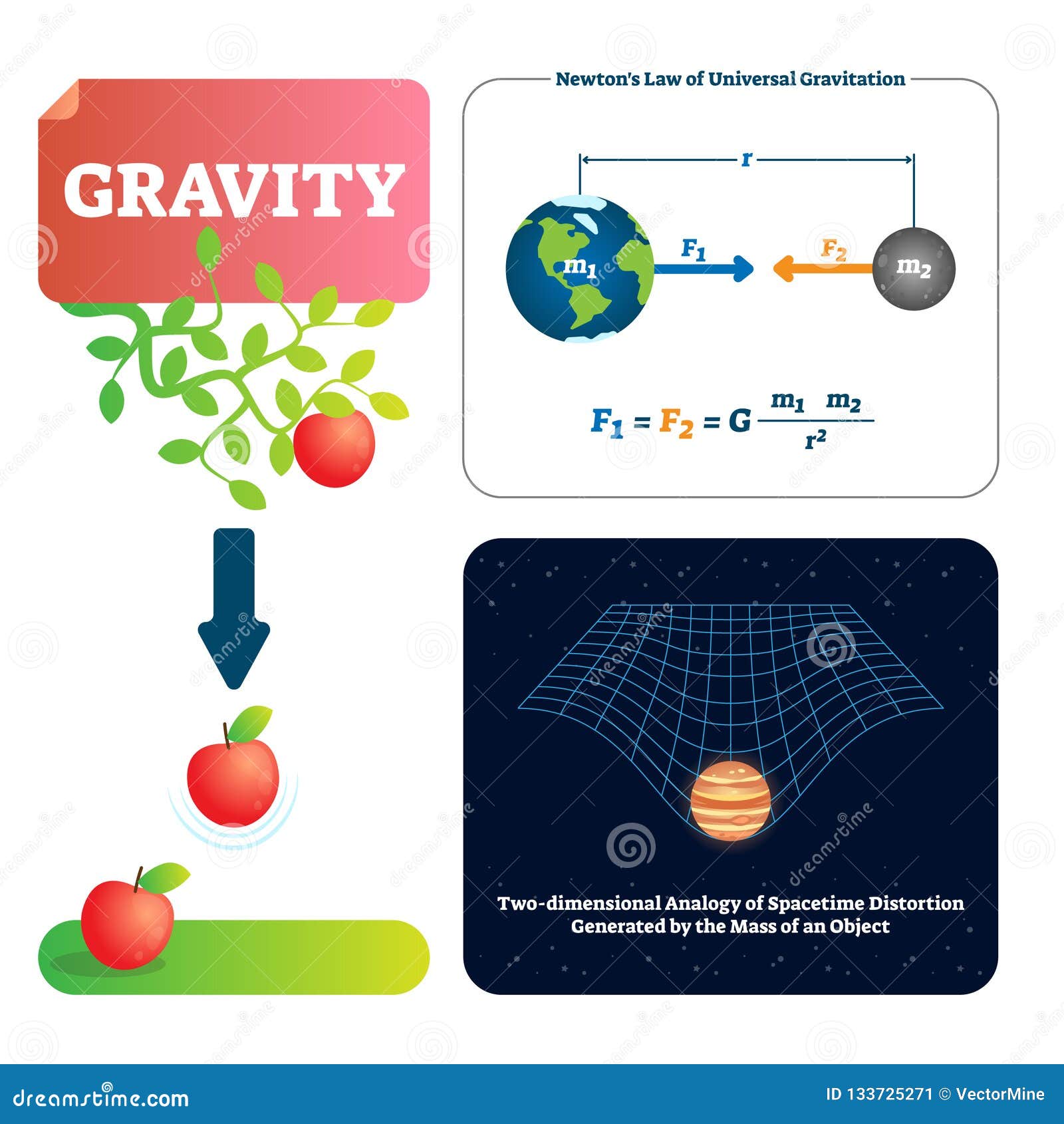
The 9.8 m/s^2 is the acceleration of an object due to gravity at sea level on earth. You get this value from the Law of Universal Gravitation. Force = m*a = G (M*m)/r^2. Here you use the radius of the earth for r, the distance to sea level from the center of the earth, and M is the mass of the earth.
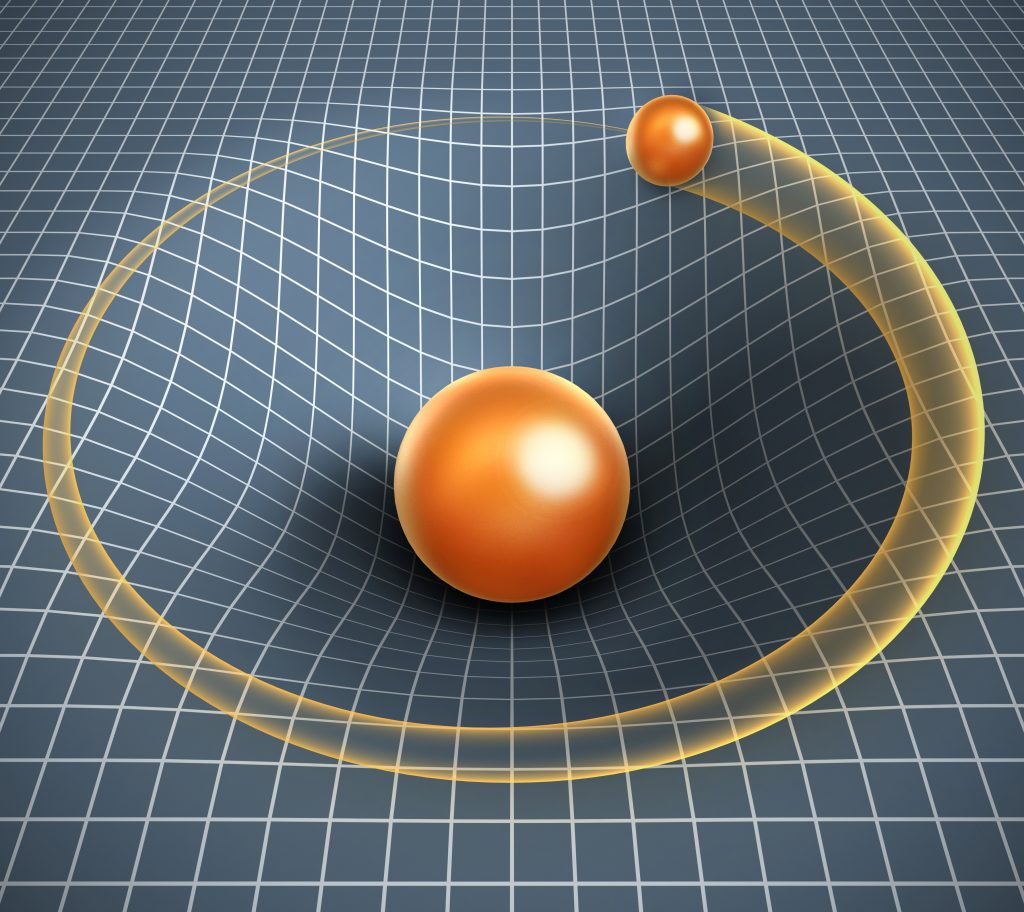
The Gravity of Natural Law Wholeness
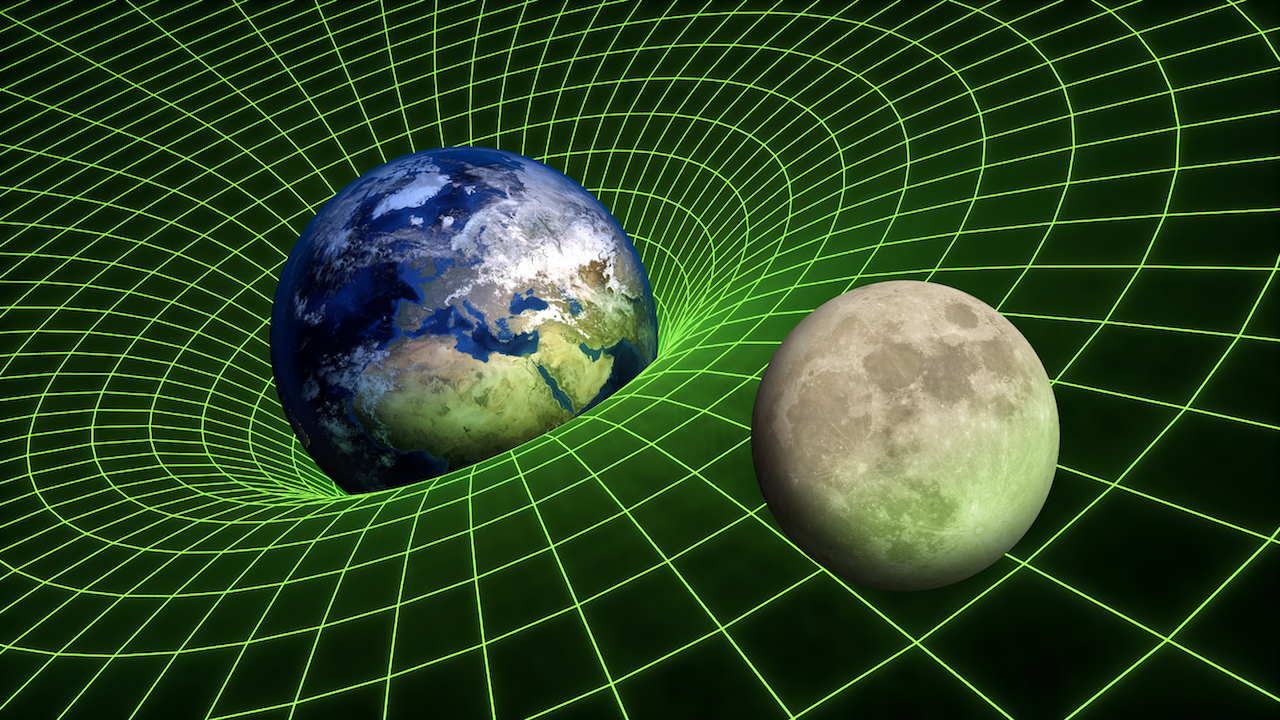
Gravity is just geometry, the result of the curvature by massive objects of the space and time around them. The strength of the gravitational " field " at any point in space or time is just.
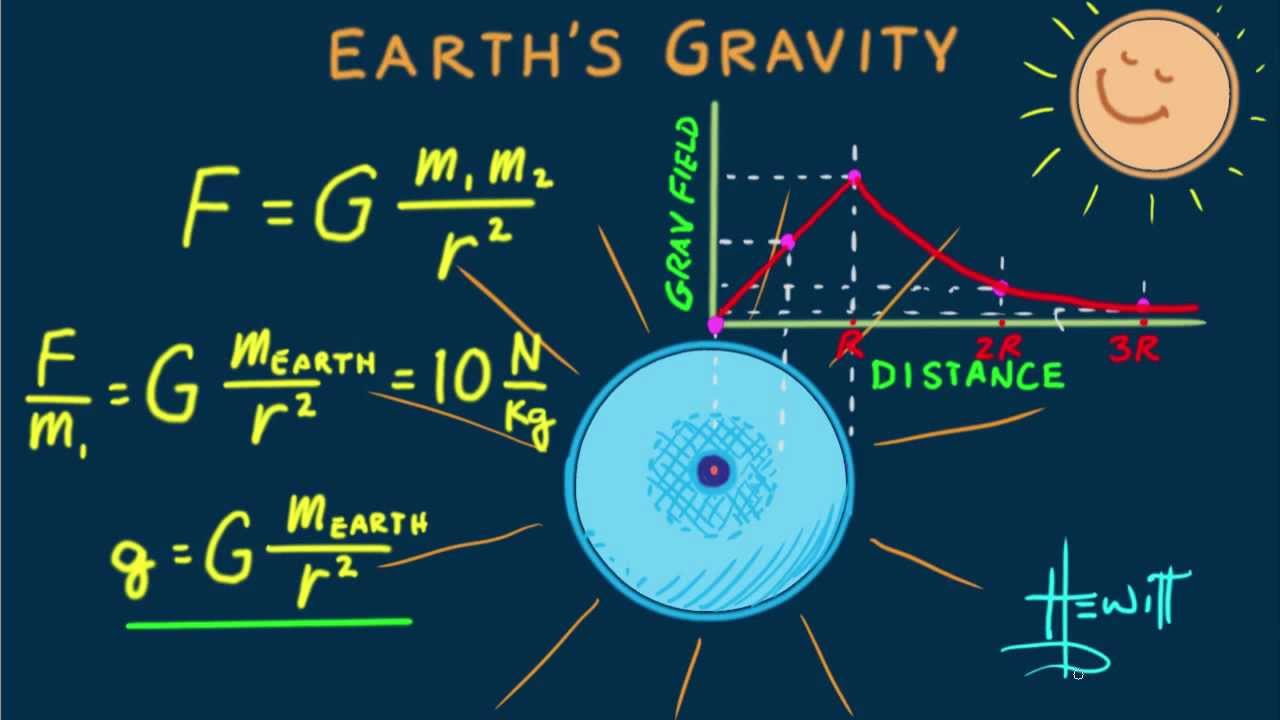
How Much Gravity Is On Earth
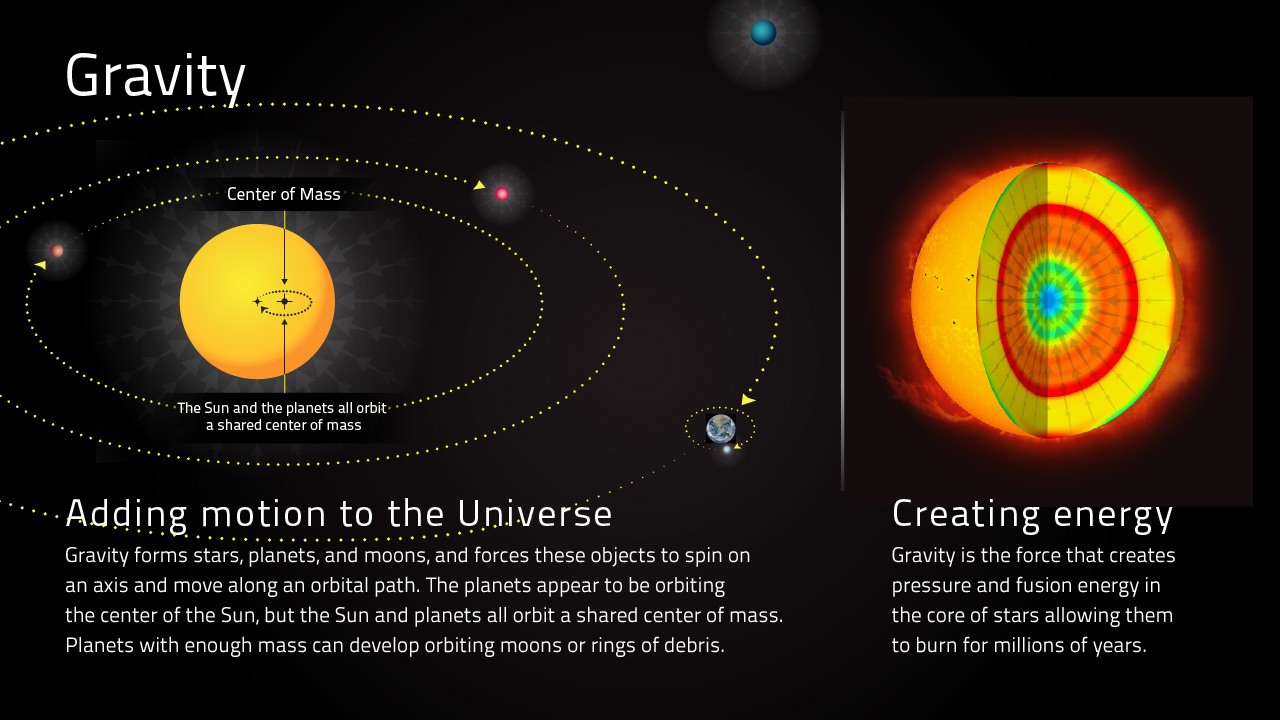
Gravity or gravitation is a natural phenomenon by which all things with energy are brought toward (or gravitate toward) one another, including stars, planets, galaxies, and even light and sub-atomic particles. Gravity is responsible for many of the structures in the universe, by creating spheres of hydrogen—where hydrogen fuses under pressure to form stars—and grouping them into galaxies.

DROPS OF ENGLISH NATURAL SCIENCE GRAVITY
Humans only recently (like in the last 300 years) realized what Gravity is all about. Greek philosophers thought that the planets and stars were part of the gods' realm and followed a "natural motion." They did not realize that Gravity is involved. The Greeks' ideas stuck around until the 16th century.

Gravity by joliannroom402
Gravity - Force, Physics, Theory: The Newtonian theory of gravity is based on an assumed force acting between all pairs of bodies—i.e., an action at a distance. When a mass moves, the force acting on other masses had been considered to adjust instantaneously to the new location of the displaced mass. That, however, is inconsistent with special relativity, which is based on the axiom that all.

gravity Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
Gravity is the gravitational attraction at the surface of a planet or other celestial body; "gravity" may also include, in addition to gravitation,. (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy). In this book, Newton described gravitation as a universal force, and claimed that "the forces which keep the planets in their orbs must [be.
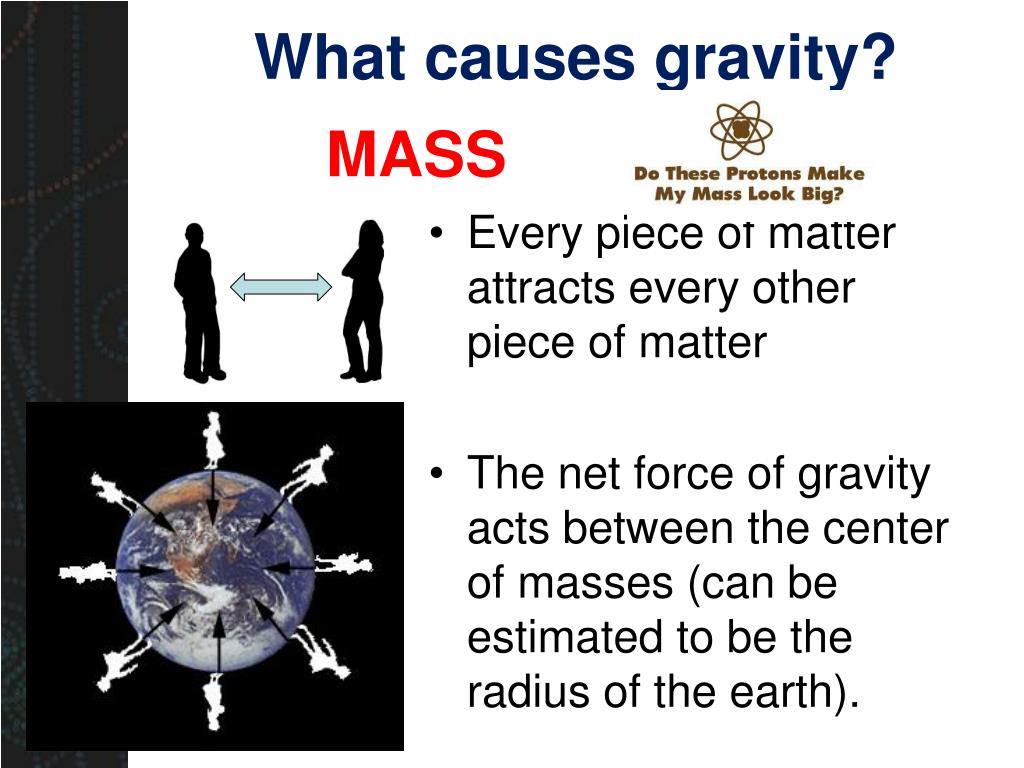
PPT Gravity PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3042616
Everyone knows that what goes up must come down. But why? Gravity, it turns out, is full of surprises…

What is gravity? Live Science
Gravity is the force that keeps us grounded. NASA used a Lunar Landing Walking Simulator to study astronauts' ability to perform tasks whilst experiencing one-sixth of normal gravity in.

Why is gravity important for our lives? Curiosity Guide Science
gravity, in mechanics, the universal force of attraction acting between all matter. It is by far the weakest known force in nature and thus plays no role in determining the internal properties of everyday matter. On the other hand, through its long reach and universal action, it controls the trajectories of bodies in the solar system and elsewhere in the universe and the structures and.
Gravity Phenomenon Infographic Diagram Showing How An Object Of Low Mass Is Pulled By
Gravity. The natural phenomenon by which physical bodies appear to attract each other with a force proportional to their masses. It is most commonly experienced as the agent that gives weight to objects with mass and causes them to fall to the ground when dropped. The phenomenon of gravitation itself, however, is a byproduct of a more.

The Bouguer gravity anomaly means that gravity is not evenly distributed Boing Boing
Verlinde's analysis indicates that gravity emerges from physical dynamics analogous to basic thermodynamic processes. "Using only. concepts like energy, entropy and temperature," he.

What Is Gravity In Science / › gravity definition science for kids.
Gravity is a natural force that that attracts a body towards the center of the earth, or towards another physical body which has mass. If an object has mass it also has gravity, and the extent to.

general relativity What is gravity and what causes objects to act against it? Physics Stack
Gravity is what holds the planets in orbit around the sun and what keeps the moon in orbit around Earth. The gravitational pull of the moon pulls the seas towards it, causing the ocean tides. Gravity creates stars and planets by pulling together the material from which they are made. Gravity not only pulls on mass but also on light.
Fundamental Forces of Nature Multiwavelength Astronomy
There was no real explanation of why or how. Gravity was just the way it was, and Newton's Laws of Gravity were mainly predictive, not explanatory. [At least the ancients had an explanation. Objects (air, earth, fire and water) sought their natural place in the ordered scheme of things - as if they had minds of their own obeying cosmic laws.